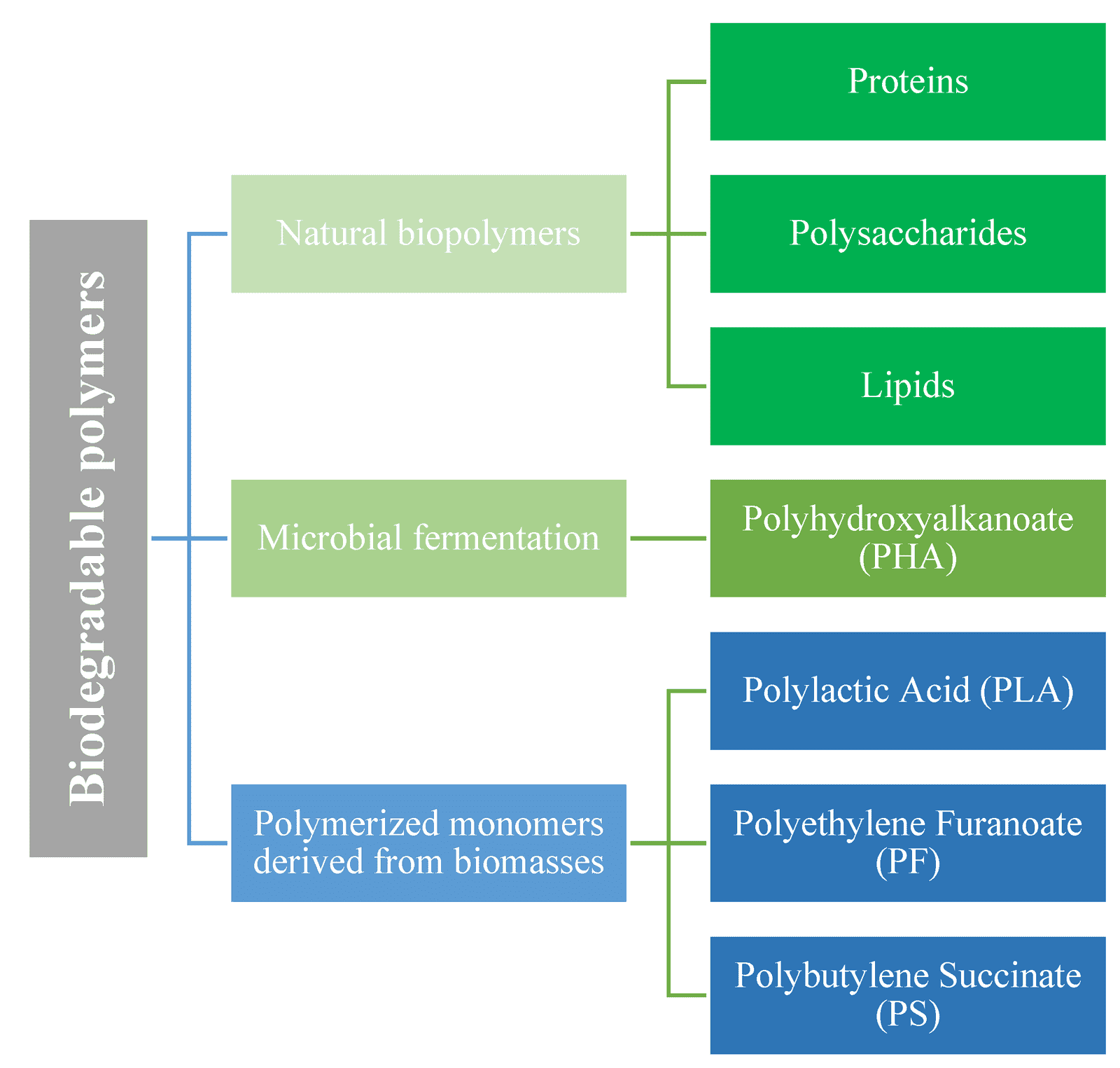
Biodegradable waste decomposes naturally, while non-biodegradable waste does not. Biodegradable items break down over time by biological processes; non-biodegradable ones persist in the environment.
Understanding the difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste is crucial for environmental health and sustainability. Biodegradable waste consists of organic materials like food scraps, paper, and wood that can be easily broken down by microorganisms within a reasonable time frame.
For students in Class 4, distinguishing these types requires recognition of natural decomposition. Non-biodegradable waste comprises plastics, metals, and glass, materials that require hundreds to thousands of years to decompose, if at all, thus posing a significant challenge to waste management. Grasping these concepts helps children appreciate responsible waste disposal and the importance of recycling in protecting our planet. Reducing the amount of non-biodegradable waste we produce and increasing our reliance on biodegradable materials can lead to a healthier environment for all living beings.
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Biodegradable Waste: Nature’s Recyclables
Imagine nature as a big, amazing recycler. It takes biodegradable waste and turns it into something useful. When we say something is biodegradable, it means it can be broken down by nature. Leaves, food scraps, and paper are all things that nature can handle. This is great for our planet!
The Circle Of Life: How Biodegradables Break Down
Biodegradable waste goes through an exciting process. Tiny things we can’t even see, like bacteria and fungi, eat up this waste. Worms and insects help too. They all work together, breaking it down into nutrients that go back into the soil. This helps new plants to grow. It’s like the waste gets a new life!
Organic Matter: Key Components Of Biodegradable Waste
Let’s peek at what’s in biodegradable waste. It’s mostly organic matter, which is stuff that comes from living things.
- Food scraps: Like apple cores and banana peels
- Plant parts: Such as leaves and twigs
- Paper products: Made from trees, like napkins and cardboard
These organic materials break down easily, making them special recyclables that go right back to nature.

Credit: pubs.acs.org
Nonbiodegradable Debris: A Stubborn Legacy
Waste comes in all shapes and sizes, but some refuse to go away. Nonbiodegradable waste is the kind that stays in our environment for years, even centuries, without breaking down. Items like plastic bags, styrofoam, and metal cans don’t mix well with nature. They turn into a stubborn legacy that our planet struggles with.
Lingering Impact: Resistance To Natural Processes
Unlike their biodegradable cousins, nonbiodegradable materials are resistant to natural decay processes. This resistance means they remain intact in landfills and ecosystems, creating longer-term environmental challenges:
- Wildlife entanglement and ingestion
- Soil and water contamination
- Landscape disfiguration
Plastics And Metals: Prime Examples Of Nonbiodegradables
Examples that illustrate the problem with nonbiodegradables come in the form of plastics and metals:
| Material Type | Common Items | Environmental Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Plastics | Bottles, bags, straws | Poisonous chemicals, long-lasting litter |
| Metals | Cans, foil, appliances | Resource depletion, habitat destruction |
Other materials such as glass and certain synthetics also contribute to this nonbiodegradable legacy, posing a threat to global sustainability efforts.
Comparing Decomposition: Timelines And Environments
An understanding of how different wastes decompose helps us make smarter choices. It’s like comparing apples and oranges to look at the timelines and natural settings of biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste. This knowledge can guide us to protect our planet better.
Speed Of Decay: Fast For Bio, Slow For Non-bio
Biodegradable items break down easily. They can turn into soil in months or even days. Nature works fast on them! Think of banana peels or leaves in a compost bin. On the other side, non-biodegradable items don’t play nice with nature. Plastics or metals can stay unchanged for hundreds of years. They need special treatment to go away.
Habitat Footprints: Ecosystem Effects And Disruptions
Different waste types don’t just sit there—they interact with their homes. Biodegradable waste can be part of life cycles, feeding plants or creatures. But, it can also be harmful if there’s too much. Non-biodegradable waste often harms homes for wildlife. It can travel through water or land, causing even more problems.
- Biodegradable Waste:
- Mixes into the soil
- Can be composted
- Supports new plant growth
- Non-Biodegradable Waste:
- Doesn’t mix with nature
- Lasts a long time without change
- Potential danger to animals and plants
Impact Of Waste On The Environment
Waste can change our Earth. It’s because some waste breaks down, but some does not. How waste affects nature depends on this. Let’s dive into the roles of biodegradable and nonbiodegradable waste and their effects.
Pollution And Toxicity: Long-term Effects Of Nonbiodegradables
Nonbiodegradable waste stays for a very long time. It does not blend into the earth. It creates pollution that harms air, water, and soil.
- Plastic bottles can take 450 years to break down.
- Chemicals from nonbiodegradables seep into water, making it unsafe.
- Animals mistake these for food, which can make them sick or even end their lives.
These wastes stack up in landfills and oceans, causing a big mess.
Enhancing Soil: The Positive Role Of Biodegradable Waste
Biodegradable waste is kind to Earth. It breaks down naturally and turns into compost.
| Biodegradable Item | Time to Decompose |
|---|---|
| Apple Core | 1-2 months |
| Paper | 2-6 weeks |
| Leaves | 1 month |
This compost acts as food for plants. It makes the soil healthy and rich for farming.
- Nature turns leftover food into useful compost.
- Trees and plants grow better with this natural fertilizer.
People can help nature by making their own compost at home.
Progress Towards Sustainability
In the journey for a greener Earth, different types of waste play separate roles. Understanding the difference between biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste is key for class 4 students. It shapes the future of our planet. Learning this instills sustainable habits early on. Let’s explore some exciting changes and smart practices that help in managing waste sustainably.
Innovations In Waste Management
New methods are changing how we handle trash. Here are a few:
- Composting: Turns kitchen scraps into garden food.
- Bio-digesters: These special tanks break down organic matter.
- Recycling robots: They sort recycling faster than humans.
These innovations help us use resources wisely. They turn our waste into useful stuff. This is good for our world!
Promoting Eco-friendly Habits From A Young Age
It’s great to start good habits young. Here is how young students can help:
- Use less paper to save trees.
- Bring a reusable water bottle to school.
- Recycle and compost in the classroom.
When kids practice these actions, they grow up to be earth-friendly adults. They also encourage families and friends to be better too. This creates a healthier planet for everyone.

Credit: pubs.acs.org
Making Eco-smart Decisions: A Class 4 Mantra
Welcome to our young eco-warriors’ guide on making the planet greener. “Making Eco-Smart Decisions: A Class 4 Mantra” is not just a catchphrase, it’s the way forward for our fourth graders to understand the difference between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable waste. Let’s dive into how our future leaders can actively engage in eco-friendly practices at school and take them into their homes and communities.
Active Participation: School Programs And Activities
Our schools are the starting line for championing environmental awareness. Participating in school programs plants the seed for appreciating our Earth. Activities can include:
- Recycling drives to collect paper, plastic, and metal.
- Composting workshops teaching waste breakdown.
- Crafting sessions using recycled materials.
- Competitions for the most eco-friendly classroom.
Interactive lessons on sorting waste help kids understand how different materials decay. Materials like apple peels become part of the soil quickly. They are biodegradable. Plastic bags do not blend back into the earth easily. They are nonbiodegradable. These school activities encourage our children to make greener choices.
Home And Community: Transferring Knowledge To Action
Eco-friendly habits start in the classroom, but they flourish at home. Kids can lead the change through:
- Setting up home recycling bins with labels for sorting waste.
- Starting a small compost bin for kitchen scraps.
- Making and using eco-bags for shopping.
- Teaching family members about reducing waste.
Community-wise, young minds can share what they’ve learned. They can organize neighborhood clean-ups. Or, they can start gardening clubs to grow more plants. Actions like these make BIG differences for our planet.
Frequently Asked Questions Of What Is The Difference Between Biodegradable And Nonbiodegradable Waste Class 4
What Defines Biodegradable Waste?
Biodegradable waste consists of organic material that can decompose naturally. Examples include food scraps, paper, and yard clippings. Bacteria, fungi, and other organisms break these down into simpler substances.
Why Is Some Waste Non-biodegradable?
Non-biodegradable waste can’t be broken down by natural processes. It’s typically made of synthetic materials like plastics and certain chemicals. This type of waste can persist in the environment for years, causing pollution.
What Are The Impacts Of Biodegradable Waste?
Biodegradable waste, when managed properly, enriches soil and reduces landfill usage. However, if it decomposes anaerobically (without oxygen) in landfills, it emits methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
How Does Non-biodegradable Waste Affect Ecosystems?
Non-biodegradable waste accumulates in ecosystems, leading to pollution. It harms wildlife, clogs waterways, and disrupts natural habitats. Over time, it can also leach toxic substances into soil and water.
Conclusion
Understanding the distinction between biodegradable and nonbiodegradable waste is crucial for our planet’s health. By educating ourselves on these differences, we empower our young scholars to make informed decisions. Let’s embrace eco-friendly practices and instill sustainable habits in our children, setting a foundation for a greener future.
Together, we can create a cleaner world for generations to come.