Biodegradable materials in landfills decompose slower due to limited oxygen. They may release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, during breakdown.
Understanding the lifecycle of biodegradable materials is crucial for environmental sustainability. While many consumers believe that biodegradable items naturally break down quickly even when disposed of in landfills, the reality is a bit more complex. Landfills typically compact waste, creating an anaerobic environment that slows down the degradation process.
As a result, materials that would ordinarily decompose swiftly in nature can take much longer in a landfill setting. During the slow breakdown process, biodegradable waste can generate methane, contributing to climate change. Knowing this helps inform better waste management practices and the promotion of composting and recycling as more eco-friendly alternatives to landfill disposal. It emphasizes why individual choices about waste can have significant environmental impacts.
The Journey Of Biodegradables To Landfills
The journey of biodegradable materials to landfills is a complex process. It’s crucial to understand what occurs once our biodegradable waste is thrown away. Let’s unravel the life cycle of biodegradable items. From the moment they’re disposed of, to their arrival at the landfill.
From Trash Bin To Burial Site
Every piece of biodegradable waste has a story. It starts in our homes or offices, where we drop it into the trash bin thinking it’ll simply decompose. But the truth is quite different.
- Collection: Waste management services collect our trash.
- Sorting: Some places sort recyclables and biodegradables.
- Transport: Trucks take unsorted waste directly to landfills.
In the landfill, lack of oxygen and sunlight alters the decomposition rate. Thus, the expectation that biodegradables will break down quickly is often mistaken.
Types Of Biodegradable Materials
Diverse materials claim the ‘biodegradable’ label. Here’s a quick look at what they might include:
| Material | Examples |
|---|---|
| Organic Waste | Fruit peels, food scraps |
| Paper Products | Newspaper, cardboard |
| Plant-Based Materials | Cornstarch packaging, plant-derived plastics |
Not all biodegradables are equally eco-friendly. Some require specific conditions to decompose effectively. Thus, landfills might not be the ideal spot for these materials to break down.

Credit: www.mdsassociates.com
Decomposition In A Landfill Environment
When we bury biodegradable materials in landfills, we often assume they will just decompose. Yet, this process is complex. Let’s explore what really happens in a landfill environment.
The Role Of Microorganisms
In decomposition, microorganisms play a key role. These tiny life forms break down organic matter. They turn waste into simpler compounds. But in landfills, their work gets tricky.
- Not enough oxygen can slow them down.
- Different microbes work at various stages.
- Their activity affects how fast waste breaks down.
Anaerobic Vs. Aerobic Breakdown
Aerobic processes need oxygen. They’re fast and efficient. In contrast, anaerobic processes don’t. They happen in oxygen-poor landfill layers.
| Aerobic Breakdown | Anaerobic Breakdown |
|---|---|
| Uses oxygen | Does not use oxygen |
| Produces CO2 | Produces CH4 (methane) |
| Quick decomposition | Slow decomposition |
Landfills mostly see anaerobic breakdown. This is slower and creates methane, a potent greenhouse gas. Poor conditions can stall the breakdown for years.
Factors Affecting Biodegradation Rates
Unlocking the secrets behind the decay of biodegradable materials in landfills starts with understanding the factors that affect biodegradation rates. These elements interact in complex ways, influencing how quickly organic materials break down. Knowing these factors helps us improve landfill management and reduce environmental impact.
Presence Of Oxygen And Moisture
Oxygen and moisture are essential in the degradation process of biodegradable materials. When materials are buried, they may not get enough air. Without oxygen, the decay slows down significantly. This process, called anaerobic decomposition, produces methane, a potent greenhouse gas. The right moisture level is vital as well. Too little moisture hampers microbial activity, while too much can create harmful leachates.
- Air flow impacts biodegradation rate.
- Methane is created from oxygen-limited decay.
- Ideal moisture levels are crucial for breakdown.
Temperature And Ph Levels
Temperature spikes accelerate chemical and biological processes. Warm conditions boost microbial activity, which speeds up decomposition. On the other hand, cold temperatures can slow the process to a near halt. pH levels also govern the speed of biodegradation. Microbes thrive at neutral pH values. Any extreme in pH can suppress their efficiency, delaying material breakdown.
- Higher temperatures increase decomposition speed.
- Colder conditions slow down microbial action.
- pH levels influence microbe effectiveness.

Credit: eco-mdsassociates.com
Landfill Challenges And Biodegradable Waste
People sometimes think that biodegradable materials are fine to bury in landfills. Yet, they face many challenges once buried. Let’s explore what happens to these materials and why they might not break down as expected.
Lack Of Ideal Conditions
In nature, biodegradable items break down with the help of sunlight, air, and microorganisms. In the thick layers of a landfill, these helpful elements are scarce. Buried without access to air or moisture, biodegradable items don’t find the ideal conditions they need to break down. Instead, they might linger for years, much like their non-biodegradable counterparts.
Generation Of Methane Gas
When biodegradable waste finally breaks down in a landfill, it often does so anaerobically (without oxygen). This process can create methane, a powerful greenhouse gas. Methane contributes to climate change much more aggressively than carbon dioxide. Landfills can capture some methane for energy, but not all of it, meaning the rest escapes into the atmosphere, harming our planet.
- Landfills block sunlight: No decomposition with solar energy.
- Layers suffocate waste: No air means no aerobic breakdown.
- Moisture is trapped: Dry conditions prevent decomposition.
- Methane released is potent: Bad for climate, even in small amounts.
| Condition | Role in Decomposition | Presence in Landfills |
|---|---|---|
| Sunlight | Accelerates breakdown | None |
| Air | Needed for aerobic processes | Very limited |
| Moisture | Helps microorganisms thrive | Often too low |
| Methane Gas | Byproduct of anaerobic breakdown | High generation |
The path of biodegradable materials in landfills is complex and filled with obstacles. Understanding this helps us see why proper waste management is essential for our environment.
The Impact Of Landfill Management
The Impact of Landfill Management on biodegradable materials is significant. When we bury organic waste, a complex process unfolds. Understanding how landfills manage these materials is key to mitigating environmental issues.
Leachate Production And Control
What’s leachate? It’s the liquid that drains from a landfill. As biodegradable materials break down, this liquid forms and can harm the environment.
Landfills need proper lining systems to prevent leachate from seeping into the ground. Monitoring wells and treatment systems are also essential. They detect and manage leachate leaks.
- Leachate collection systems: Pipes and drains that capture the liquid for treatment.
- Liner technology: Layers of plastic or clay that guard against leaks.
- Treatment plants: Facilities that clean the collected leachate.
Innovations In Landfill Technology
There are exciting advances in landfill technology that aim to make waste management more efficient and less harmful to the planet.
Bioreactor landfills enhance the breakdown of organic matter. They use added moisture and air to speed up decomposition. This method also increases the production of landfill gas for energy.
| Innovation | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Bioreactor Landfills | Controlled injection of air/water | Faster decomposition, renewable energy |
| Gas Collection Systems | Capture of methane for fuel | Reduces greenhouse emissions |
| Solar Covers | Generates solar energy | Offsets landfill energy usage |
Solar covers not only cap landfills but also harness solar energy. This technology serves a dual purpose — containing waste and generating power.

Credit: www.bloomberg.com
Embracing Sustainable Disposal Methods
Biodegradable materials promise a greener planet. When buried in landfills, they face challenges. These materials require oxygen, sunlight, and microbes to break down. Landfills, unfortunately, lack these elements. This leads to a slow decomposition process and the production of methane, a harmful greenhouse gas. To address this, sustainable disposal methods gain focus.
People and industries turn to greener methods to manage waste. These methods include composting and the use of bioplastics. Composting converts organic waste into nourishing soil. Bioplastics offer a reduced carbon footprint. Together, they represent a shift towards sustainable practices.
Composting As An Alternative
Composting stands out as a key solution for biodegradable materials. It involves natural processes that recycle organic material. This process enhances soil health and reduces landfill waste. Composting requires a balance of green and brown materials, moisture, and oxygen.
- Green materials are rich in nitrogen, such as food scraps.
- Brown materials provide carbon, like dry leaves.
Balancing these elements ensures efficient breakdown of material. The result is nutrient-rich compost. This compost can support plant growth and reduce the reliance on synthetic fertilizers.
The Rise Of Bioplastics
Bioplastics emerge as a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics. Made from renewable resources, their production often requires less fossil fuel. This makes their carbon footprint smaller. Bioplastics can decompose under the right conditions, reducing environmental impact.
| Type of Bioplastic | Source Material | Environmentally Friendly Feature |
|---|---|---|
| Polylactic Acid (PLA) | Cornstarch | Compostable in commercial facilities |
| Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA) | Microbial fermentation of sugars | Biodegrades in soil and water |
Consumers and businesses focus on the use of bioplastics. This trend suggests a significant shift in how society approaches plastic production and waste.
Frequently Asked Questions On What Happens To Biodegradable Materials That Are Buried In Landfills
Do Biodegradable Materials Decompose In Landfills?
Biodegradable materials may decompose in landfills, but at a slower rate. Without proper sunlight, oxygen, and microorganisms, degradation is inhibited, leading to potential methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
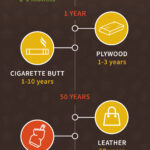
How Long Do Biodegradable Items Take To Break Down?
The decomposition of biodegradable items varies; in landfills, it can take years. Factors like material type, landfill conditions, and item thickness affect the breakdown time. Under ideal conditions, some items may decompose within weeks or months.
What Factors Affect Biodegradation In Landfills?
Biodegradation in landfills is influenced by moisture, temperature, landfill design, and waste composition. Lack of oxygen and microbial activity slows down the process compared to open, compost-like environments.
Does Burial Hinder Biodegradable Waste Decomposition?
Yes, burial in landfills can hinder the decomposition process. Biodegradable waste requires oxygen for microbes to efficiently break it down, which is scarce in buried, compacted environments. This can lead to incomplete decomposition and methane production.
Conclusion
Wrapping up, biodegradable materials in landfills face a complex journey. Lacking proper conditions, they struggle to decompose effectively, adding to environmental concerns. Responsible waste management and composting emerge as crucial solutions. Together, we can ensure biodegradables fulfill their eco-friendly promise.
Embrace change for a sustainable future.