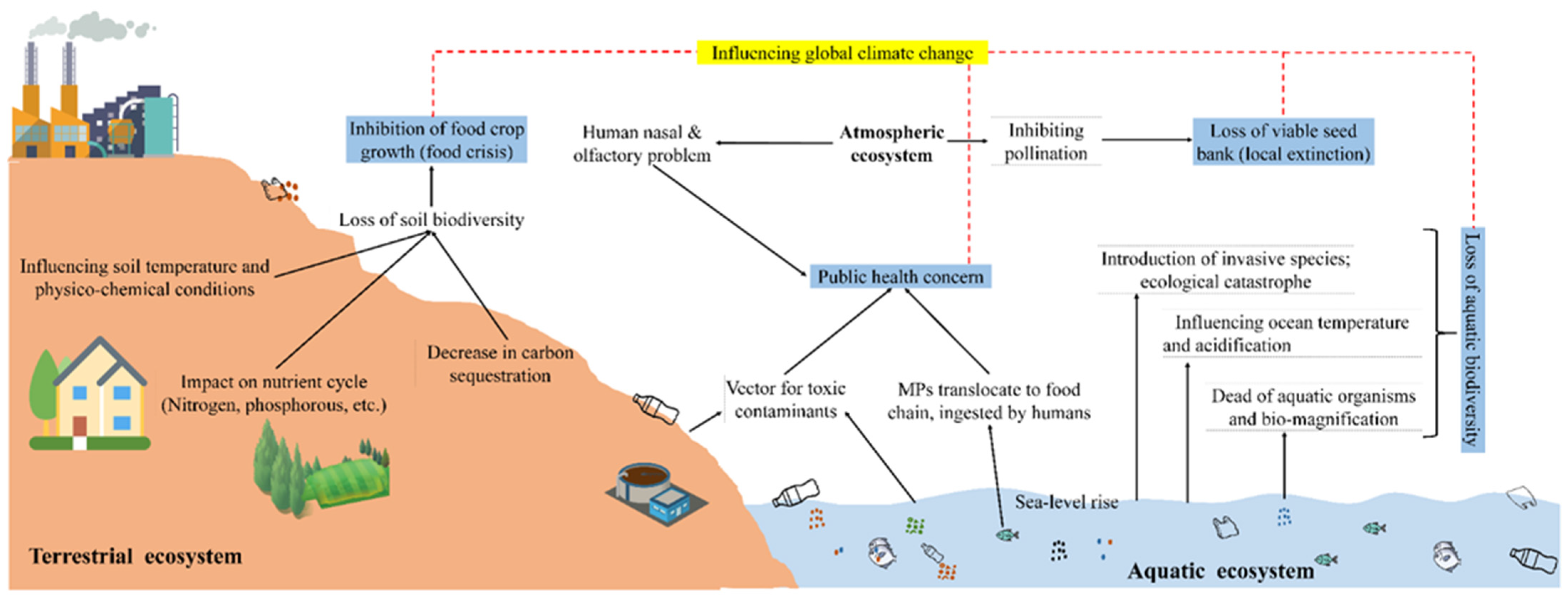
Biodegradable plastics can cause environmental harm and confusion in waste management. Breakdown conditions for these plastics are often not met in natural settings.
Exploring the challenges posed by biodegradable plastics offers insight into the complexities of eco-friendly materials. These plastics, designed to decompose more quickly than conventional plastics, seem like an ideal solution to plastic pollution. Yet, their degradation relies heavily on specific industrial processes, not always available or efficient.
Even in optimal conditions, biodegradable plastics may release methane, a potent greenhouse gas, exacerbating climate change issues. Consumers often misunderstand the difference between biodegradable, compostable, and regular plastics, leading to improper disposal. Recycling systems struggle as biodegradable plastics can contaminate the recycling stream, compromising the quality of recycled materials. This broad overview highlights the pressing need for a critical assessment of so-called sustainable alternatives and robust infrastructure to handle their unique disposal requirements.

Credit: link.springer.com
Introduction To Biodegradable Plastics
As the world seeks eco-friendly alternatives to traditional plastics, biodegradable plastics have emerged as a promising solution. These materials promise to return to the earth without leaving a lasting mark. Yet, they come with complex challenges that need careful analysis. This post unpacks the problems of biodegradable plastics by diving into their nature and the expectations set upon them.
Definition and Composition of Biodegradable PlasticsDefinition And Composition Of Biodegradable Plastics
Biodegradable plastics differ from regular plastics in their ability to break down. With the help of microorganisms and environmental conditions, they decompose into natural substances like water, carbon dioxide, and biomass. These plastics are often made from renewable raw materials like corn starch, cellulose, and certain oils. This composition encourages the breakdown process once the product has served its purpose.
The Rise of Biodegradable Plastics and Environmental PromisesThe Rise Of Biodegradable Plastics And Environmental Promises
In recent years, biodegradable plastics have surged in popularity. Companies and consumers alike see them as an answer to waste accumulation and environmental harm. Products like shopping bags, packaging, and disposable tableware made from biodegradable materials are now more common. They are marketed on the premise that they can reduce the impact of plastic waste on the natural world.
Misconceptions And Misleading Claims
The buzz around biodegradable plastics suggests an eco-friendly solution to waste. Yet, beneath the green veneer lie several issues. Misconceptions and misleading claims cloud our understanding of these materials. Let’s uncover the truth behind so-called eco-friendly plastics.
Understanding Biodegradation And Environmental Conditions
Biodegradable plastics should break down naturally. But, for them to decompose, specific conditions are necessary. These include the right temperature, moisture, and biological activity. Without these factors, biodegradable plastics may persist like traditional plastics.
- Temperature: Most require industrial composting facilities.
- Moisture: They need enough but not too much.
- Biological Activity: Microorganisms must be present.
The Issue With Labeling: ‘biodegradable’ Vs. ‘compostable’
There is frequent confusion between ‘biodegradable’ and ‘compostable’. These terms aren’t interchangeable.
‘Biodegradable’ means a product can break down without a timeframe. ‘Compostable’ products require specific settings and time to decompose.Many believe if a product is biodegradable, it is also compostable. This is not always true. Accuracy in labeling is crucial for proper disposal.
| Term | Definition | Required Conditions |
|---|---|---|
| Biodegradable | Breaks down naturally | Varies widely |
| Compostable | Decomposes in composting conditions | Specific moisture, temperature, timeframe |
Misleading Marketing And Consumer Confusion
Companies often use green terms to sell products. The term ‘biodegradable’ is a marketing favorite. But without context, it misleads. Consumers might discard items in nature thinking they will decompose. Reality is, without the right conditions, they won’t. This misunderstanding can lead to increased pollution.
Education is key. Knowledge of disposal and degradation processes helps consumers make informed decisions. It ensures biodegradable plastics serve their intended purpose. Without transparency, the cycle of misinformation continues.
Environmental Impact And Management Challenges
The environmental impact and management challenges of biodegradable plastics make their “eco-friendly” label questionable at times. While these materials promise to reduce the burden on landfills, their real-world implications are complex.
Lack Of Adequate Industrial Composting Facilities
Biodegradable plastics require specific conditions to decompose properly. Many regions lack the industrial composting facilities needed for this process. As a result, these materials often end up in landfills where they do not degrade efficiently, thus contributing to pollution and waste management issues.
Biodegradable Plastics In Marine Environments
These plastics pose a threat to our oceans. They break down at a slower rate in cooler, marine waters, leading to accumulation. This accumulation endangers marine life as they mistake these materials for food or become entangled in them.
Consequences For Wildlife And Ecosystems
- Birds, fish, and other animals confuse small biodegradable plastic pieces for food.
- Consumption can lead to toxic side effects, internal injuries, or death.
- Natural habitat disruptions occur as these plastics break down irregularly in the environment.
The Carbon Footprint Of Biodegradable Plastics Production
Producing biodegradable plastics still generates greenhouse gases. In some cases, the emissions during the production and breakdown of these materials rival those of traditional plastics. This counteracts the perceived benefits and adds to the ongoing climate crisis.

Credit: www.pinterest.com
Economic And Policy Considerations
While biodegradable plastics pose as more eco-friendly, their economic and policy-related issues challenge widespread adoption. Cost production, global infrastructural disparities, and complex regulations demand critical attention.
The Cost Implications Of Producing Biodegradable Plastics
Despite the environmental appeal, biodegradable plastics come at a steep price. Traditional plastics, derived from petroleum, enjoy economies of scale. In contrast, biodegradable variants require expensive organic materials and advanced technology to produce. This elevates manufacturing costs significantly, often translated to higher prices for consumers. Below is a table highlighting key cost factors:
| Material Source | Technology Needs | Production Scale | Consumer Price Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Organic/Renewable | Advanced | Smaller | Higher |
Global Disparities In Waste Management Infrastructure
Effective disposal of biodegradable plastics hinges on advanced waste management systems. Countries vary greatly in their capabilities. Wealthier nations may boast sophisticated infrastructure that can handle these materials. Developing regions, however, often lack the necessary systems, resulting in improper disposal and potential environmental harm. Biodegradable plastics require special conditions to degrade, which are not universally available, complicating global efforts toward eco-friendliness.
Policy And Regulatory Frameworks Governing Biodegradable Plastics
Regulations surrounding biodegradable plastics are complex and ever-changing. Governments must craft policies that encourage their use while ensuring that standards for degradation are met. Conflicting international standards can create barriers to market entry, stifling innovation and competition. Policymakers face the task of developing clear, enforceable guidelines that align with environmental goals without imposing excessive burdens on producers and consumers.
Future Perspectives And Alternative Solutions
The road to sustainable materials is paved with challenges, yet holds a promise for a greener future. Biodegradable plastics have been touted as an eco-friendly solution, but they come with their issues, including decomposition rate concerns, the need for specific conditions to break down properly, and the creation of microplastics. As we examine Future Perspectives and Alternative Solutions, various strategies emerge to tackle these problems head-on, promising a cleaner and more sustainable world for future generations.
Research And Development Of New Materials
Breaking free from traditional plastics, researchers tirelessly seek new materials that degrade efficiently and safely. Innovative bioplastics from renewable sources like starch or cellulose demonstrate promising features. Biopolymers not always require oxygen to decompose, making these materials more versatile and earth-friendly.
Consumer Behavior And The Shift Towards Circular Economies
The push towards reusable and renewable products drives consumer behavior towards a circular economy. In this model, products and materials are recycled continuously, reducing waste and the need for new resources.
- Educating shoppers about sustainable choices
- Incentivizing the return and reuse of products
- Supporting businesses that prioritize sustainability
Innovations In Recycling And Waste Management
Technological advancements in recycling processes ensure biodegradable plastics don’t end up in landfills. Composting facilities and specialized recycling programs tailor solutions to manage these materials better, turning them back into valuable resources.
Global Initiatives And Cooperative Efforts
Addressing the plastic dilemma is a global mission. Countries unite to form regulations and promote practices reducing the negative impacts of bioplastics. International alliances also empower innovations and share successful strategies for a broader reach and impact.
- Formulation of universal grading standards
- Exchange of recycling technologies across borders
- Joint environmental initiatives and educational campaigns
Credit: www.mdpi.com
Conclusion: Navigating The Eco Dilemma
Biodegradable plastics promise a greener planet but come with issues. We must find balance. This balance involves understanding materials, real-world limits, and resulting environmental impacts. By diving into sustainable materials and their real-world challenges, we’ll explore actionable steps for all stakeholders. This includes the pivotal role of education and awareness.
Reconciling The Need For Sustainable Materials With Real-world Issues
Sustainable materials are vital for our planet. Yet, their benefits vary. Some break down only under specific conditions. Others leave behind microplastics. We need clearer standards for what truly counts as biodegradable.
Actionable Steps For Consumers, Industries, And Governments
- Consumers can opt for reusable alternatives and support eco-conscious brands.
- Industries should invest in R&D for better biodegradable plastics and transparent labeling.
- Governments can create stricter regulations and incentives for using sustainable materials.
The Role Of Education And Awareness In Mitigating The Eco Dilemma
Understanding the pros and cons of biodegradable plastics is key. Education drives better choices. Awareness campaigns can inform public decisions. Schools can incorporate sustainability into curricula. Knowledge empowers action.
Frequently Asked Questions For What Are The Problems With Biodegradable Plastics
What Are The Disadvantages Of Biodegradable Plastics?
Biodegradable plastics have several disadvantages, including higher production costs compared to traditional plastics. They often have a shorter lifespan, which can be unsuitable for some uses. Biodegradability can vary under different environmental conditions, potentially leading to inconsistent decomposition rates. These plastics can also contribute to methane emissions if not composted properly.
What Are The Problems With Bioplastics?
Bioplastics may not fully decompose, potentially requiring specific conditions to break down. They can also compete with food production for land and resources and may not always be as sustainable as advertised, depending on their lifecycle and the types of materials used.
What Are The Threats Of Biodegradable Plastic?
Biodegradable plastics can threaten ecosystems if not managed properly. They may require specific conditions to decompose, potentially leading to accumulation in environments. Also, they might contribute to microplastic pollution if they break down improperly.
How Biodegradable Plastics Affect The Environment?
Biodegradable plastics can reduce landfill waste, as they decompose faster than traditional plastics. Yet, if not processed correctly, they may not fully break down and can still contribute to pollution and harm wildlife.
Conclusion
Understanding the challenges with biodegradable plastics is crucial. These materials aren’t a perfect solution. They require specific conditions to break down and can contribute to pollution if not managed properly. Our responsibility is to seek better alternatives and improve waste management systems.
It’s a step towards sustainable living, and every effort counts.